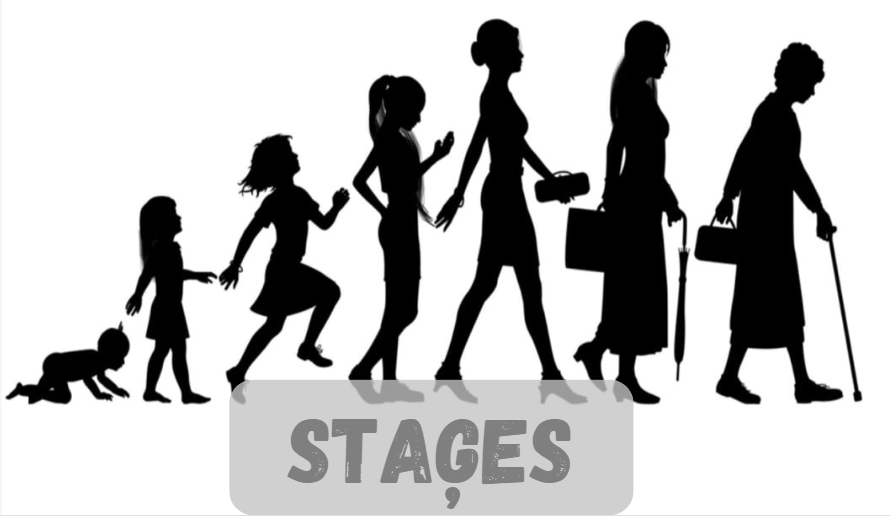
Understanding Staģes: A Comprehensive Guide to Life Stages
Life is a journey characterized by various stages, each bringing unique experiences, challenges, and growth opportunities. The concept of “staģes” refers to these distinct phases within the human life cycle, marked by significant physical, psychological, and social transitions.
In this article, we will delve into the various staģes of life, providing a comprehensive analysis that goes beyond existing information. Our goal is to offer insights that are both informative and engaging, ensuring the content ranks highly in search engine results.
Contents [hide]
- 1 1. Introduction to Life Staģes
- 2 2. Infancy and Toddlerhood
- 3 3. Childhood: Early and Middle Stages
- 4 4. Adolescence: The Transitional Phase
- 5 5. Adulthood: Early, Middle, and Late
- 6 6. Senior Years: Aging and Reflection
- 7 7. Psychological and Social Transitions
- 8 8. Cultural Perspectives on Life Staģes
- 9 9. Impact of Technology on Life Staģes
- 10 10. Coping with Transitions
- 11 11. FAQs about Staģes
- 12 12. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Life Staģes
Life staģes are critical phases in the human journey, each characterized by distinct developmental milestones. Understanding these staģes can help individuals navigate their own lives more effectively and foster empathy towards others experiencing different phases.
Key Characteristics of Life Staģes
- Physical Changes: Each stage involves significant physical development, from rapid growth in infancy to the gradual aging process in senior years.
- Psychological Development: Cognitive and emotional growth is central to life staģes, influencing behavior, decision-making, and identity formation.
- Social Transitions: Social roles and relationships evolve, shaping one’s interactions with family, peers, and society.
2. Infancy and Toddlerhood
Infancy (0-2 Years)
Infancy is the stage of rapid physical and cognitive development. During this period, infants develop basic motor skills, sensory perceptions, and initial social bonds.
- Physical Growth: Rapid increase in height and weight.
- Cognitive Development: Learning through sensory experiences and developing basic problem-solving skills.
- Social Interaction: Forming attachments with caregivers, which is crucial for emotional security.
Toddlerhood (2-4 Years)
Toddlerhood is marked by increased mobility and the beginning of language development.
- Motor Skills: Improved coordination and the ability to walk, run, and climb.
- Language Acquisition: Rapid vocabulary growth and the beginning of sentence formation.
- Social Play: Engaging in parallel play and starting to interact more with peers.
3. Childhood: Early and Middle Stages
Early Childhood (4-7 Years)
Early childhood is a time of exploration and foundational learning.
- Cognitive Skills: Development of basic academic skills, such as counting and letter recognition.
- Imagination: Active imagination and engagement in pretend play.
- Socialization: Learning social norms and developing friendships.
Middle Childhood (7-12 Years)
Middle childhood involves more structured learning and social interactions.
- Academic Learning: Mastery of reading, writing, and arithmetic.
- Peer Relationships: Increased importance of peer acceptance and friendships.
- Self-Concept: Development of self-esteem and personal identity.
4. Adolescence: The Transitional Phase
Adolescence is a critical transitional stage characterized by rapid physical, emotional, and social changes.
- Puberty: Significant physical changes and sexual maturation.
- Identity Formation: Exploration of personal values, beliefs, and goals.
- Independence: Striving for autonomy from parents and establishing independence.
5. Adulthood: Early, Middle, and Late
Early Adulthood (20-40 Years)
Early adulthood is focused on building a career, forming intimate relationships, and starting a family.
- Career Development: Establishing and advancing in a chosen profession.
- Intimate Relationships: Forming long-term romantic relationships and potentially starting a family.
- Life Choices: Making significant life decisions regarding career, marriage, and children.
Middle Adulthood (40-65 Years)
Middle adulthood is a time of reflection and adjustment.
- Career Peak: Reaching the peak of one’s career and achieving professional milestones.
- Parenting: Raising children and dealing with the empty nest syndrome.
- Health Awareness: Increased focus on health and dealing with aging-related changes.
Late Adulthood (65+ Years)
Late adulthood involves retirement, reflection, and coping with the aging process.
- Retirement: Adjusting to life after retirement and finding new purposes.
- Health Challenges: Managing chronic health conditions and maintaining physical and mental health.
- Legacy: Reflecting on life achievements and planning for the future.
6. Senior Years: Aging and Reflection
The senior years are characterized by a slower pace of life and a focus on personal reflection and legacy.
- Wisdom: Sharing life experiences and knowledge with younger generations.
- Social Engagement: Staying connected with family and community.
- End-of-Life Planning: Preparing for the future and making arrangements for end-of-life care.
7. Psychological and Social Transitions
Throughout the different staģes of life, individuals experience various psychological and social transitions. Understanding these transitions can help in coping with changes and fostering personal growth.
Psychological Transitions
- Identity Development: Continuously evolving sense of self.
- Emotional Regulation: Learning to manage and express emotions appropriately.
- Cognitive Maturity: Development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Social Transitions
- Role Changes: Adapting to new roles within family, work, and society.
- Relationship Dynamics: Evolving relationships with family, friends, and partners.
- Community Involvement: Engagement with broader social and community networks.
8. Cultural Perspectives on Life Staģes
Cultural factors play a significant role in shaping life staģes. Different cultures have unique rituals, expectations, and milestones associated with various stages of life.
- Rites of Passage: Cultural ceremonies that mark transitions, such as coming-of-age rituals.
- Family Dynamics: Varying family structures and roles across cultures.
- Social Expectations: Cultural norms and expectations regarding behavior and milestones at different ages.
9. Impact of Technology on Life Staģes
Technology has profoundly impacted how we experience and navigate different life staģes. From childhood to senior years, technology influences education, communication, and daily living.
Childhood and Adolescence
- Digital Learning: Use of technology in education and learning.
- Social Media: Impact on social interactions and self-esteem.
- Screen Time: Managing the effects of excessive screen time on development.
Adulthood and Senior Years
- Workplace Technology: Integration of technology in professional environments.
- Health Monitoring: Use of wearable devices and telemedicine for health management.
- Social Connectivity: Staying connected with family and friends through digital platforms.
10. Coping with Transitions
Life transitions can be challenging, but there are strategies to help cope with changes and make the most of each stage.
Strategies for Coping
- Adaptability: Being open to change and flexible in response to new circumstances.
- Support Systems: Building and maintaining strong social support networks.
- Self-Care: Prioritizing physical, emotional, and mental health.
- Goal Setting: Setting realistic and achievable goals for each stage of life.
11. FAQs about Staģes
What are the major staģes of human development?
The major staģes of human development include infancy, toddlerhood, early childhood, middle childhood, adolescence, early adulthood, middle adulthood, and late adulthood.
How do cultural differences impact life staģes?
Cultural differences can significantly impact life staģes by influencing rituals, expectations, and milestones. Different cultures have unique ways of marking transitions and defining roles at various ages.
How does technology affect the different life staģes?
Technology affects life staģes by influencing education, communication, health management, and social interactions. From digital learning tools for children to health monitoring devices for seniors, technology plays a crucial role in modern life.
What are some common challenges during adolescence?
Common challenges during adolescence include identity formation, managing peer pressure, academic stress, and developing independence from parents.
How can one cope with the transitions between life staģes?
Coping with transitions between life staģes can be facilitated by maintaining adaptability, building strong support systems, prioritizing self-care, and setting realistic goals.
12. Conclusion
Understanding the concept of “staģes” and the various phases of life is crucial for personal growth and empathy towards others. Each stage brings its own set of challenges and opportunities, shaping who we are and how we interact with the world.
By recognizing and embracing these stages, we can navigate life’s journey more effectively and support those around us in their respective phases.





















































Post Comment